- August 28, 2025
- Mins Read
Hue is the all-in-one coloring utility that you’ll ever need.
Usage
Hex
You can easily use hex colors with the init(hex:) convenience initializer on UIColor. It supports the following hex formats #ffffff, ffffff, #fff, fff
let white = UIColor(hex: “#ffffff”)
let black = UIColor(hex: “#000000”)
let red = UIColor(hex: “#ff0000”)
let blue = UIColor(hex: “#0000ff”)
let green = UIColor(hex: “#00ff00”)
let yellow = UIColor(hex: “#ffff00”)
Computed color properties
let white = UIColor(hex: “#ffffff”)
let black = UIColor(hex: “#000000”)
if white.isDarkColor {} // return false
if white.isBlackOrWhite {} // return true
Alpha
.alpha is a sugar for colorWithAlphaComponent, internally it does the exact same thing, think of it as a lipstick for your implementation.
let colorWithAlpha = myColor.alpha(0.75)
Gradients
You can easily create gradient layers using the gradient() method on arrays with UIColor. As an extra bonus, you can also add a transform closure if you want to modify the CAGradientLayer.
let gradient = [UIColor.blackColor(), UIColor.orangeColor()].gradient()
let secondGradient = [UIColor.blackColor(), UIColor.orangeColor()].gradient { gradient in
gradient.locations = [0.25, 1.0]
return gradient
}
Image colors
let image = UIImage(named: “My Image”)
let (background, primary, secondary, detail) = image.colors()
Components
You can get red, green, blue, and alpha components from any UIColor by using the (red|green|blue|alpha)Component property.
let myColor = UIColor(hex: “#ffafc2”)
let myColorBlueComponent = myColor.blueComponent
let myColorGreenComponent = myColor.greenComponent
let myColorRedComponent = myColor.redComponent
let myColorAlphaComponent = myColor.alphaComponent
Blending
let red = UIColor.redColor()
let green = UIColor.greenColor()
let yellow = red.addRGB(green)
let desaturatedBlue = UIColor(hex: “#aaaacc”)
let saturatedBlue = desaturatedBlue.addHue(0.0, saturation: 1.0, brightness: 0.0, alpha: 0.0)
Supporting the project
If you want to support the development of this framework, you can do so by becoming a sponsor. ❤️
Examples
Hex
This super simple example that displays a bunch of color schemes in a Carousel view.
It uses hex to set the color for the schemes. It leverages from .isDarkColor to make the text color readable in all scenarios.
The demo also features Spots for rendering the Carousel view.
Example code:
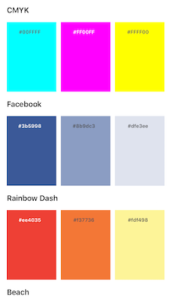
let color = UIColor(hex: “#3b5998”)
backgroundColor = color
label.textColor = color.isDark
? UIColor.whiteColor()
: UIColor.darkGrayColor()
Gradients
This examples shows how much fun you can have with combining CAGradientLayer with CABasicAnimation.
It uses .hex for getting the colors and .gradient() for transforming a collection of UIColor‘s into a CAGradientLayer.
The demo features Spots for rendering the list view and Fakery for generating random content strings.
Extract from the demo:

lazy var gradient: CAGradientLayer = [
UIColor(hex: “#FD4340”),
UIColor(hex: “#CE2BAE”)
].gradient { gradient in
gradient.speed = 0
gradient.timeOffset = 0
return gradient
}
Installation
Hue is available through CocoaPods. To install it, simply add the following line to your Podfile:
pod ‘Hue’
Hue is also available through Carthage. To install just write into your Cartfile:
github “hyperoslo/Hue”
To install Hue using Swift Package Manager with Xcode 11, just follow the instructions at https://developer.apple.com/documentation/swift_packages and import the platform specific library to the project:
import Hue
GitHub
- August 27, 2025
- SwiftUI
This package provides you with an easy way to show tooltips over any SwiftUI view, since Apple does not provide ...
- August 27, 2025
- SwiftUI
- Uncategorized
SimpleToast is a simple, lightweight, flexible and easy to use library to show toasts / popup notifications inside iOS or ...
- August 27, 2025
- SwiftUI
Create Toast Views with Minimal Effort in SwiftUI Using SSToastMessage. SSToastMessage enables you to effortlessly add toast notifications, alerts, and ...




