- August 28, 2025
- Mins Read
About
ExpyTableView is a re-write based on SLExpandableTableView. Takes some ideas, concepts and codes and regenerates them in Swift. Lets you create expandable table views as easily as its ancestor.
With ExpyTableView, you make an expandable table view by using multiple cells and inserting/deleting them(which can mean expanding and collapsing). With this approach, you will have a great chance in future design requests. All you will have to do is adding a new UITableViewCell and writing the code for it. You will easily have the new design.
When using ExpyTableView, sections are being expanded and collapsed. You implement your table view as you always do, and add an extra method. Then your section becomes expandable.
Requirements
VERSION 1.2.2:
- SPM Support
- iOS 10.0+
- Swift 5.0+
- Objective-C compatibility
VERSION 1.2.1:
- CocoaPods version
- iOS 10.0+
- Swift 5.0+
- Objective-C compatibility
VERSION 1.0:
- iOS 8.0+
- Swift 4.0+
VERSION 0.3.1:
- iOS 8.0+
- Swift 3.0+
Installation
ExpyTableView is available through CocoaPods. To install it, simply add the following line to your Podfile:
pod ‘ExpyTableView’
Or you can manually drag and drop the ExpyTableView.swift AND ExpyAbstractions.swift into your project, then use it.
How to use
First of all, if you are using Interface Builder, set your table view’s class and module as ExpyTableView.’
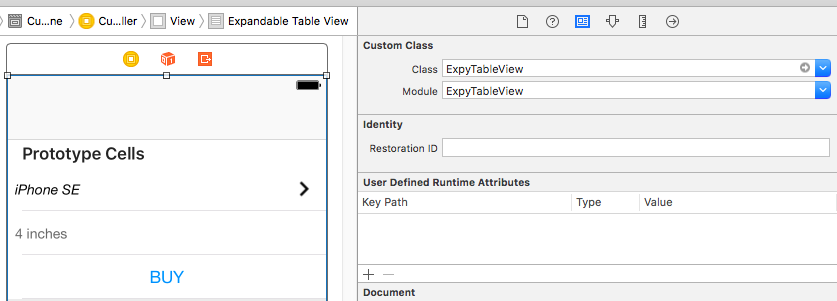
Then start implementing required methods:
import ExpyTableView
class ViewController: ExpyTableViewDataSource {
@IBOutlet weak var expandableTableView: ExpyTableView!
// First, set data source for your table view.
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
expandableTableView.dataSource = self
//Set delegate if you will implement any UITableViewDelegate or ExpyTableViewDelegate methods.
//expandableTableView.delegate = self
}
// Then return your expandable cell instance from this data source method.
func tableView(_ tableView: ExpyTableView, expandableCellForSection section: Int) -> UITableViewCell {
// This cell will be displayed at IndexPath with (section: section and row: 0)
}
}
You are ready to go with the setup above.
Customization (optional)
extension ViewController {
//OPTIONAL DATA SOURCE METHOD, default is true for all sections.
func tableView(_ tableView: ExpyTableView, canExpandSection section: Int) -> Bool {
return true //Return false if you want your section not to be expandable
}
}
You can use optional delegate method:
extension ViewController: ExpyTableViewDelegate {
//OPTIONAL DELEGATE METHOD, receives callbacks when a section will expand, will collapse, did expand, did collapse. A unified method.
func tableView(_ tableView: ExpyTableView, expyState state: ExpyState, changeForSection section: Int) {
switch state {
case .willExpand:
print(“WILL EXPAND”)
case .willCollapse:
print(“WILL COLLAPSE”)
case .didExpand:
print(“DID EXPAND”)
case .didCollapse:
print(“DID COLLAPSE”)
}
}
If your header cell (which is section: section and row: 0) conforms to ExpyTableViewHeaderCell protocol which is optional, it gets notifications in changeState method: (See example project for more detailed usage)
class YourTableViewCell: UITableViewCell, ExpyTableViewHeaderCell{
//changeState method has a cellReuse parameter to allow you to prepare your cell for reusing.
//All state info is allocated by ExpyTableView.
func changeState(_ state: ExpyState, cellReuseStatus cellReuse: Bool) {
switch state {
case .willExpand:
print(“WILL EXPAND”)
case .willCollapse:
print(“WILL COLLAPSE”)
case .didExpand:
print(“DID EXPAND”)
case .didCollapse:
print(“DID COLLAPSE”)
}
}
}
You can manually expand or collapse any section like below:
//These two methods are exposed publicly.
public func expand(_ section: Int) {}
public func collapse(_ section: Int) {}
//You can use these methods as below.
expandableTableView.collapse(0) //Collapse section at (index: 0) manually
expandableTableView.expand(1) //Expand section at (index: 1) manually
You will get callbacks for all of the UITableViewDataSource or UITableViewDelegate methods. Just conform to ExpyTableViewDataSource and ExpyTableViewDelegate and they will forward you all the methods you need.
extension ViewController{
//All of the UITableViewDataSource and UITableViewDelegate methods will be forwarded to you right as they are.
//Here you can see two examples below.
func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, didSelectRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) {
print(“DID SELECT row: \(indexPath.row), section: \(indexPath.section)”)
}
func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, heightForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> CGFloat {
return UITableViewAutomaticDimension
}
}
See example code for more details and implementation examples.
Example
To run the example project, just download the project and open the xcworkspace file in Example folder.
Roadmap
- Add a variable that allows collapsing the recently expanded section, when any other section is expanded
- Add a variable that allows scrolling to recent expanded section rect to show it completely
- Add a variable that allows clicking on any cell in section to expand or collapse the whole section
- Add expandAll and collapseAll methods and functionality
All contributions about these issues or other improvements are really appreciated.
Screenshots
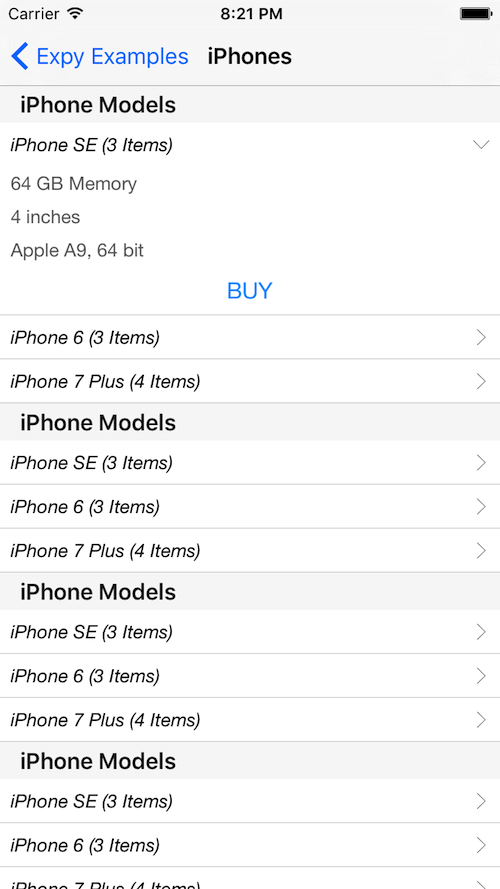
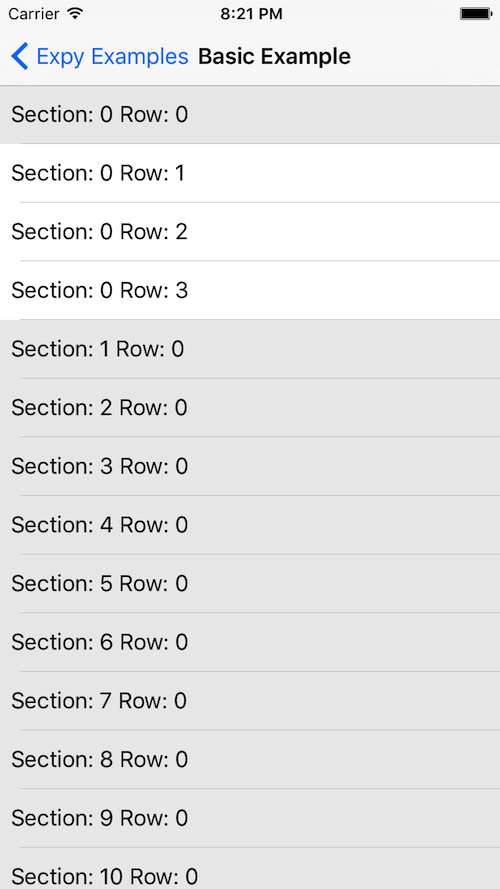
GitHub
- August 27, 2025
- SwiftUI
This package provides you with an easy way to show tooltips over any SwiftUI view, since Apple does not provide ...
- August 27, 2025
- SwiftUI
- Uncategorized
SimpleToast is a simple, lightweight, flexible and easy to use library to show toasts / popup notifications inside iOS or ...
- August 27, 2025
- SwiftUI
Create Toast Views with Minimal Effort in SwiftUI Using SSToastMessage. SSToastMessage enables you to effortlessly add toast notifications, alerts, and ...




